A decade ago, turmeric’s identity was limited to that of a spice and food additive. A few individuals still knew of its medicinal properties and traditional texts validated this point.
However, today turmeric is equivalent to gold in the nutraceutical industry.
And these properties of turmeric are extensively attributed to its bioactive ingredient, ‘Curcumin’. So one of the confusions that first arose was that should one take only curcumin or is turmeric better?
We have covered that in our article Should you take Turmeric or Curcumin: Which is better?.
Well, science keeps throwing in new terms and facts, thus giving rise to confusion and this time it is ‘curcuminoids’. Turmeric’s active components are divided into two phases: curcuminoids and oil.
So the question is ‘Is curcumin and curcuminoids the same?’. Let’s find out.
Table of Contents
What are Curcuminoids?
There are over 100 species in the Curcuma family and one thing that is characteristic of these species is the yellow orange hue. The compounds responsible for this colour are curcuminoids.
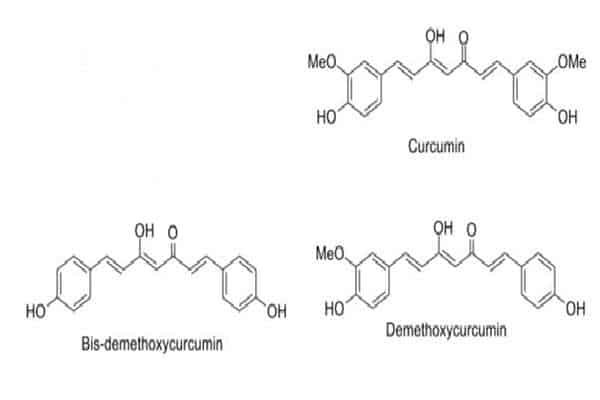
The three main curcuminoids are curcumin, bis-demethoxycurcumin, and de-methoxycurcumin. They account for 2-6% of the rhizome content (80% curcumin, 18% demethoxycurcumin and 2% bisdemethoxycurcumin). This is what their structure looks like:
Adapted from: Recent advances in the investigation of curcuminoids, Hideji Itokawa et al. Chinese Medicine 2008 3:11
Curcuminoids is also a term used for synthetic analogs and other derivatives of curcumin which possess key structural features.
Analogs of curcumin are also derived from other plant sources eg: 6-gingerol and their activities are very similar to curcumin. Primarily curcuminoids are potent antioxidants. In addition research proves that they also possess anti-inflammatory activity, anti-HIV, and anti-cancer activity.
Some studies have implicated the use of curcuminoids in treatment of stroke, adjuvant to long term opiod therapy, Alzheimer’s disease and in case of memory deficits.
The need to prepare synthetic variations of curcuminoids is that they have poor oral bioavailability and are rapidly metabolised. Over 30 metabolites of curcuminoids have been discovered from human samples after having consumed curcuminoids.
So the idea is to develop these metabolites and study their activity in order to directly provide these compounds without having to wait for metabolic reactions.
Note: Curcuminoids is the group of compounds that impart a orange yellow color to the spice. They also possess medicinal properties.
What is curcumin?
Curcumin is the principal bioactive ingredient of turmeric. It is the most important and abundant curcuminoid. Curcumin comprises 2-5% of the rhizome content.
The chemical name of curcumin, is (1E, 6E) -1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)- 1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione and it is often referred to as diferruloylmethane.
Curcumin is a powerful antioxidant. It raises the level of antioxidant enzymes and scavenges reactive oxygen species. Dietary intake of such plant derived antioxidants is considered important since it protects the body from damage by reactive oxygen species.
Its anti-inflammatory property is assumed to be linked with its antioxidant property. It inhibits the activity of enzymes and chemicals that are produced during inflammation.
Apart from these principal features, curcumin is considered as a highly pleiotropic molecule and this still remains a mystery as to how one molecule exhibit so many features and target so many biological molecules.
For example, it acts as a radiosensitizer and chemosensitizer to tumor cells and at the same time protecting normal cells from side effects of such treatments. As an anti-microbial agent, it inhibits the growth of fungi, bacteria, viruses, etc.
Some properties of curcumin are exclusive; for example its antidepressant activity, protection against cardiovascular diseases, action against cystic fibrosis, drug induced liver injury.
Other curcuminoids may show these properties but their therapeutic effect would be weak.
Among all the curcuminoids, curcumin is the most potent one but the only drawback it faces is that it is not absorbed well in the body.
Note: Curcumin is the most important curcuminoid. It is the bioactive ingredient of turmeric and demonstrates a number of pharmacological properties.
So why are the terms ‘curcumin’ and curcuminoids’ used interchangeably?
Researchers clearly differentiate between curcumin and curcuminoids but the pharma industry for simplicity sake calls all curcuminoids as curcumin.
When opting for turmeric supplements it is always recommended standardized 95% curcumin or curcuminoids.
This does not mean that 95% of the product is curcumin but rather 95% of the product contains curcuminoids. This further contains 70-80% of curcumin and the rest accounts for bisdemethoxycurcumin and demethoxycurcumin.
Why not 100% or just pure curcumin? Because it is not going to add to the potency or bioavailability but just add to extraction expenses.
A number of different formulations are made in order to make the curcuminoids more bioavailable. This table gives you a rough idea of the curcuminoid concentration present in the supplements.
|
Name |
Contents |
Bioavailability |
| Standardized 95% curcumin C95 | 95% curcuminoid mixture | – |
| Micronized Curcuminoids with turmeric oil | 95% curcuminoid mixture plus turmeric oil | 5 times greater than C95 |
| Curcuminoid phospholipid complex | 18-20%curcuminoids 40% phosphatidylcholine | 30 times better than curcuminoids and 20 times better than curcumin |
| Curcuminoid cyclodextrin complex | 2:1 cyclodextrin curcuminoid complex 14% curcuminoids | 45 times better absorption than C95 |
| Lipid curcumin particles | 20-30% total curcuminoids, lipids, and other inert materials | 65 fold better absorption than free curcumin |
| Dispersed nanoparticle curcumin | 10%curcumin, 2% other curcuminoids, glycerine, gum ghatti, water | 27 times better than free curcumin |
| Hydrophilic carrier dispersed curcuminoids | 20% curcuminoids, water-soluble carriers, and fat | 45.9 more bioavailable than curcumin |
Despite of reduction of curcuminoid concentration in the newer formulations the additional components increase the absorption of curcumin and other curcuminoids and this is better than absorption of older formulations of curcuminoids.
Conclusion
I hope this article has cleared the confusion of curcumin and curcuminoids.
Curcuminoids are a group of compounds that impart the golden yellow pigment to Curcuma species and curcumin is the most important curcuminoid.
For convenience sake, manufacturers use the terms interchangeably but from the scientific point of view, they are not the same. Any supplement stating that it has 95% standardized curcumin intends to say that 95% of the composition is curcuminoid mixture.


Will be grateful if the content is written in simple language I mean non biological language for better understanding for people like us
It appears you have gotten some of your information for your comparative table from this study:
Beyond Yellow Curry: Assessing Commercial Curcumin Absorption Technologies.
Found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25856323
Concerning the article’s comparative table comparing absorption rates, I do not see which one has the pepper or piperine added, which is discussed extensively on your website. Is it not included because the study didn’t include it?
Hi. Yes, that study does not take into account the effect of piperine on curcumin’s bioavailability. Here is the study that compares absorption of curcumin with or without piperine: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9619120
this is the inherent problem with the so called nutraceutical industry. the explanations are almost always nebulous when it comes to their “science.” For instance how can one prove that “Some properties of curcumin are exclusive; for example its antidepressant activity, protection against cardiovascular diseases, action against cystic fibrosis, drug induced liver injury?” As a scientist when I read these kind of articles i instinctively smell a scam.
are there studies regarding the anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin(oids)? Yes, and I have talked with orthopaedic physicians who confirm this. However, it is then the neutraceuticals go off the rails. This statement, for example, “protection against cardiovascular diseases.” What in the world does that even mean? most importantly, how does any scientist provide evidence of a protective mechanism?
As a consumer we must always remain skeptical of the “helps support, or protects against, prevents, or outright cures this illness or that chronic malady.” Science has yet to prove these things but they can provide evidence that shows a likelyhood of an improvement but please realize these studies, which are often limited, will always say these positive actions occur in a certain percentage of the respondents and/or participants.
we say that all people are alike and it’s true we share many similarities but in one very important aspect we are all very different and that is the fine points and nature of our biochemistry. As such, each individual will respond to a drug, food, or nutraceutical differently. sometimes this is dramatic and other times subtle and everything in between. which raises the point, if an advertised nutraceutical says it will treat/cure a laundry list of illnesses, then buyer beware. If it sounds too good to be true, it is. i am not saying don’t try this or that substance but we must temper our expectations and be skeptical.
curcuminiods 98, means it contains 98% more absorption power than normal curcumin,or does it mean 98% of the composition is curcuminiod mixture.
The essential oil of Curcuma longa contains a sesquiterpènes, Ar-curcumène.
How is this molecule relates to cucumin or cucuminoids?
Thank you for kind answer!
Very interesting and informative. I am using turmeric powder for quite some time. You mentioned that its color is golden yellow but in my country the powder is dark brown colored. Does this indicate that it is old stock or there are some other defects. If it is harmful then should I stop using it ? Will be thankful for your guidance.
Hi Mohammad. Turmeric powder is a bright orange or golden yellow in color. If its brown that means it could be a blend of other spices what is known as ‘garam masala’ in hindi. In case you suspect adulteration, here is how you could check for adulteration of turmeric spice:
https://www.turmericforhealth.com/general-info/how-to-test-turmeric-powder-for-quality-and-avoid-adulterated-products
In ny view, the problem with the curcumin vs. curcuminoids conversation is that it loses sight of the fact that whole turmeric root contains an unbeatable synergy of curcumin, curcuminoids, essential oils and hundreds of other beneficial, bioactive compounds. The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Super concentrating one or a few parts of turmeric, such as curcumin,, operates with the mistaken view that if some is good, more is better. Not true: 2 Tylenol cures headache, 200 kills you from liver falure. Supplement companies promote extracted products based on increased bioavailability, etc but the reality is that these products can be patented, whereas whole turmeric cannot, so it’s in their financial interest to do so. Incorporating turmeric in the diet is the best choice, but if not possible, choose an organic, whole turmeric powder supplement.
Thank you for this insight. Absolutely whole turmeric is best and safe in terms of health benefits.
I am taking turmeric powder of one table spoon with one pinch of black pepper with warm water of 200 Ml. is it OK or any problem-pls reply
Hi. That is absolutely fine. Though we would advise taking it right after a meal so that food an dietary fat aids in absorption. You can take Golden Paste. Start with small doses such as 1/4-1/2 tsp and if you see no side effects then increase the dose gradually to 1 tsp 2-3 times a day over a few weeks. Best taken with food to avoid acid reflux. Avoid taking it at the same time when you take meds.
http://www.turmericforhealth.com/turmeric-recipes/how-to-make-turmeric-paste-or-golden-paste
http://www.turmericforhealth.com/turmeric-recipes/how-to-make-golden-paste-from-raw-fresh-turmeric
The problem surely, is that to get a meaningful therapeutic dose of curcumin you would have to consume a huge amount of turmeric? This just isn’t practical for most people.
I have heard quite a few times, true or not but by adding fresh ground black pepper to turmeric it increases it”s absorption
True
Yes adding freshly ground black pepper increases the absorption of active ingredients of turmeric.
https://www.turmericforhealth.com/turmeric-benefits/health-benefits-of-black-pepper-and-turmeric
https://www.turmericforhealth.com/general-info/how-to-improve-bioavailability-of-turmeric
https://www.turmericforhealth.com/turmeric-queries/pepper-or-oil-which-improves-curcumins-absorption
The use of black pepper is rather like the old story of “you must drink 2 litres of water a day” which came from the Californian desert in the 1800’s. The sales gimmick of a chap who had a well! Black pepper is an irritant. Anyone taking much is quite likely to enjoy gastric problems. But as someone here has said, too much of a good thing is bad; so stick with regular doses of pure curcumin without any “accelerator” and you will be more than fine.
Hi. Studies to date have shown that pure curcumin is not well absorbed in the body. Use of black pepper as a natural bioenhancer is a part of Ayurveda- Traditional Indian Medicine and science has confirmed it’s ability to boost bioavailability of multiple therapeutic agents including curcumin.
High dose of any spice may cause gastric irritation; even researchers are not really sure as to why substances that protect the gastric mucosa should adversely affect it. It is mostly a dose-dependent effect and intake of spices in dietary amounts will protect gut health.
If an individual is susceptible to gastric irritation, he can skip black pepper and consider taking turmeric (curcumin) with dietary fat as it is fat-soluble and would be better absorbed in the body.
Black pepper will increase potency of turmeric and absorption can be only increased by coconut oil or ghee,olive oil (fats)
and such mixed paste should be taken with a meal .. easy way of doing it … I grow wild verity of turmeric in remote area of Kerala for cancer patients diet research …so we do follow latest developments in struggle to keep turmeric as a whole plant ..not divided and then promoted separated …
So is this chart based on the same dosage for each product? For example, let’s assume for a moment that C95 is 1 gram. Is the same dosage (1 gram) apply to each product listed? So 1 gram of Micronized Curcuminoids with turmeric oil 5x greater than C95… 1 gram of Lipid curcumin particles 65x greater than C95.
Some products are compared with “free cucumin”. How is the different from C95?
The chart is based on the serum concentrations of curcumin after taking each formulation based on equal concentrations of curcumin in each formulation. The curcumin content in different formulations is kept the same say 1 g but the whole capsule may have a different weight.
We will be covering this in detail in another article. And free curcumin same as C95 or standardized 95% curcumin extract.
It is true taht curcumin does not mix well with water but melts in oil. Therefore, would it not be more efficacious to simply dissolve curcumin in a warm olive oil base to maximize absorption?
Ye curcumin is poorly soluble in water but it is fat soluble. Heating curcumin in water increases its solubility by 9-12 folds. Yes curcumin in warm olive oil will increase the absorption. If you are taking supplements consuming it after the meal would help since dietary fat would take care of the absorption.