Cancer of the brain is common in older dogs; but these days its prevalence is increasing in young dogs too.
Brain tumor typically means a mass in the brain but generally is used to describe cancerous mass.
These tumors arise in the brain tissue, nerves connecting to the brain, brain envelopes or even glands located near the brain.
Certain breeds such as Boxer or Boston terrier are predisposed towards developing brain cancer.
The exact cause of brain tumor in dogs is not known.
Exposure to radiation, carcinogens in meat, solvents, pesticides or traumatic head injury and genetic factors predisposes the dog to brain tumor.
Some of the common primary brain tumors in dogs include meningioma, glioma, choroid plexus papilloma, pituitary adenoma or adenocarcinoma, astrocytoma, glioblastoma, etc.
These differ based on the cells affected.
Secondary brain tumors occur as a result of metastasis from other cancers of different origin. Symptoms of brain tumor include:
- Change in behaviour and unusual aggression
- Seizures
- Head rotation or tilt
- Blindness or vision problems
- Abnormal gait or stance
- Circling
- Loss of appetite
- Nose bleed
- Lethargy
Definite diagnosis requires CT or MRI imaging. Treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Palliative therapy is provided such as anti-seizure drugs, steroidal medications etc.
Table of Contents
- How does turmeric help fight brain tumors?
- Dosage
- Precautions
- Conclusion
How does turmeric help fight brain tumors?
Turmeric is a spice that has been used medicinally since ancient times. Today science confirms its role as an anti-cancer agent. It has a number of other pharmacological properties that aid in cancer treatment. Curcumin is its principal bioactive constituent.
Dog models of cancer, on the other hand, demonstrate similar features as human cancer. This suggests that drugs used to treat human cancer as well as findings related to them could be used in treating dog cancer.
1. Curcumin kills brain tumor cells
Research suggests that curcumin acts against various type of brain tumor cells; few of which are listed below.
Glioma

Curcumin exerts a toxic effect on glioma cells by regulating the hedgehog signalling pathway- a biochemical pathway that participates in metastasis and tumor formation.
It also destroys stem cells that cause glioma.
It sensitizes malignant glioma cells to cancer immunotherapy (a therapy in which the immune system is modulated to fight cancer). Other curcuminoids also exert anti-cancer activity against glioma.
Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of brain cancer that occurs in astrocytes- a type of star-shaped brain cells. It is a type of glioma.
Curcumin serves as a toxic agent against human astrocytoma cells. Animal studies suggest that it reduces brain inflammation caused by astrocytoma cells.
Nuclear factor kappaB is a master protein that regulates inflammation, cell growth, and survival and other processes.
Research shows that curcumin reduces the activity of nuclear factor kappa B and induces apoptosis or cell death in malignant astrocytoma cells.
Kim et al have proven that curcumin inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinases enzyme that is essential for astrocytoma metastasis.
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma multiforme is a malignant form of glioma.
Various studies suggest that curcumin is an effective anti-cancer agent in case of glioblastoma:
- It arrests the growth of glioblastoma cells in the developmental stages of the cell cycle.
- Inducing autophagy- a type of cell death
- Regulating genes involved in tumor formation
- Cutting off blood supply to tumors
Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendroglioma is a type of cancer that occurs in oligodendrocytes- a type of cells belonging to the nervous system that provide support and insulation to nerve cells. They are a type of neuroglia.
In their paper ‘Curcumin blocks brain tumor formation’ Purkayastha et al report that solubilized curcumin inhibit the growth oligodendrooglioma cells.
Further, their findings suggest that curcumin shows anti-cancer activity against neuroblastoma (a type of brain cancer), lung cancer and melanoma.
It does so by activating enzymes that cause cell death and suppressing factors that could contribute to cell survival. Researchers suggest that an injectable formulation of curcumin should be developed with the purpose of treating brain cancer.
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma is a type of brain cancer that arises in adrenal glands which originate from the same tissue as nerve cells and lie on top of the kidneys. It is further classified into various types.
Animal study shows that curcumin can inhibit growth and proliferation of neuroblastoma cells; thus serving as anti-cancer as well as a chemopreventive agent.
Curcumin analogs (compounds with the structure derived from curcumin) are found to inhibit growth of neuroblastoma cells without affecting normal stem cells.
A study reports that curcumin nanoparticles can induce cell death in neuroblastoma cells.
Medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a rare type of brain cancer in dogs and affects the cerebellum- the lower rear portion of the brain. It can metastasize and affects other tissues of the nervous system.
Curcumin inhibits growth and metastasis of medullablastoma cells by reducing the activity of cell survival factors.
Khaw et al have shown that curcumin exerts anti-tumor activity in medulloblastoma cells by arresting their growth and inducing cell death. Another mechanism involved is the suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway- a biochemical pathway involved in cell growth and survival.
Quite a number of studies demonstrate the different mechanisms by which curcumin terminates medulloblastoma cells.
Curcumin nanoparticles inhibit the growth of malignant brain tumors like medulloblastoma and glioblastoma.
Meningioma
Meningioma is a tumor of the envelopes covering the brain and spinal cord or meninges.
Curic et al studied the effect of curcumin on human meningioma cells. Curcumin treatment inhibited the growth of meningioma cells by arresting their cell growth in developmental stages.
Additionally, curcumin also induced apoptosis (cell death) by activating caspases-enzymes that support cell death and other factors in meningioma cells.
Pituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenoma is the tumor arising in the pituitary gland, a pea-sized gland lying at the base of the brain. This gland secretes hormones that regulate various activities in our body like blood pressure and metabolism. It is a very common type of brain cancer in dogs.
A study shows that curcumin attenuates growth of pituitary adenoma by inhibiting the formation of blood vessels and thereby cutting blood supply to tumors.
Other studies show that curcumin regulates hormones and inhibits the growth of hormone-producing cells of the pituitary gland in order to prevent tumor formation in the pituitary gland.
What does this mean?
Curcumin acts via multiple pathways against growth and proliferation of various kinds of brain cancers that can occur in dogs. However this data is limited to experimental lab studies as well as animal studies. Concrete studies on dogs are required to further potentiate these findings.
2. Curcumin sensitizes brain tumor cells to chemotherapy
In addition to selectively destroying cancer cells, curcumin sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents in multiple ways and prevents chemoresistance.
Glioblastoma is a type of cancer that is highly resistant to chemotherapy. Research shows that curcumin in combination with a low dose of paclitaxel(a chemotherapeutic drug) inhibits the growth of glioblastoma, chemoresistant brain tumor stem cells (stem cells are cells that have not yet differentiated into any type of cell with a specific function) and other malignant glioma cells.
Additionally, curcumin prevents these brain tumor cells from metastasizing to other parts of the body.
Research shows that curcumin has a synergistic anti-cancer effect with cisplastin and doxorubicin in inhibiting the growth of glioblastoma cells.
Curcumin and turmeric force, a nutraceutical formulation of turmeric, are proven to sensitize glioblastoma and medulloblastoma cells to chemotherapeutic agents like etoposide and temozolomide and thereby reverses drug resistance.
Curcumin does so by reducing survival signals and increasing factors that support cell death of cancerous cells.
Curcumin is also found to sensitize glioblastoma cells to radiotherapy.
What does this mean?
Curcumin reverses the resistant of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs and increases their vulnerability towards destruction by chemo and radiotherapy. This ability of curcumin can reduce the dose of chemotherapeutic drug required to treat cancer.
3. It can protect from side effects of cancer treatment
Research suggests that curcumin selectively kills cancer cells, normal cells remain unaffected.
This is not the case with conventional cancer treatment which is toxic to both normal as well as cancer cells.
Apart from serving as chemo/radiosensitizer, curcumin also works as chemo/radioprotector- when taken in combination with conventional cancer treatment, it protects normal cells and organs from damage.
Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant property is responsible for this.
Also, curcumin is proven to protect most organs- brain, stomach, kidneys, liver, lung etc. in diseased conditions in humans which serves to be therapeutic and suggestive of the fact that it can protect multiple systems from toxic effects of cancer treatment.
What does this mean?
Curcumin in combination with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy protects the rest of the body and normal organs from side effects.
4. It prevents metastasis or spread of cancer
The secondary brain tumor is quite possible- cancer spreads to the brain from another place of origin.
The most common cancers that give rise to canine brain cancer include histiocytic sarcoma and osteosarcoma. (Read Turmeric for dog histiocytic sarcoma and turmeric for dog osteosarcoma)
Also, primary brain tumor can metastasize to other parts of the body. Curcumin intake can prevent or reduce the chances of metastasis.
It suppresses tumor growth, regulates cell cycle, manipulates proteins and genes linked to cell survival, inhibits blood supply to tumors and inhibits the activity of proteins that support migration of cancer cells to other tissues.
What does this mean?
Curcumin can prevent cancer from metastasizing or spreading to other parts of the body. It can prevent primary brain tumor from spreading to different parts of the body and also prevent occurrence of secondary brain tumor or brain tumor occurring as a result of metastasis.
5. It is an anti-seizure agent
Animal studies demonstrate that curcumin has anticonvulsant property. As an antioxidant, it raises the level of antioxidant enzyme and reduces oxidative stress in the brain and reduces progression towards seizures.
In an animal model of epilepsy, curcumin supplementation due to its antioxidant potential serves as anticonvulsant agent. Combination of piperine and curcumin increases curcumin’s bioavailability.
Further, this study shows that curcumin has synergistic effect carbamazepine- an anti-epileptic drug.
Researchers have reported that curcumin increases the seizure threshold, delays the onset of seizures and reduces severity of seizures.
Phenobarbitone is a commonly prescribed anti-seizure drug to dogs in a brain tumor.
Reeta et.al. have shown that curcumin when administered with anti-seizure drugs like valproate, phenytoin, phenobarbitone and carbamazepine does not interfere in their action.
In fact, it reduces the number of drugs required for therapeutic efficacy, acts synergistically with them and also reduces the side effects caused by these medications.
What does this mean?
Curcumin, by virtue of its antioxidant property, serves as a natural anti-seizure agent. It works in combination with conventional anticonvulsants and reduces the amount of these drugs required to achieve a therapeutic effect.Curcumin also protects from side effects of these drugs.
6. It protects the brain from damage

In experimental models of brain damage, curcumin is proven to reduce inflammatory reaction and attenuate brain damage. Curcumin protects and maintains the blood-brain barrier in case of brain damage.
In models of neurotoxicity (brain-related toxic conditions), curcumin, by virtue of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory property, is found to protect the brain.
Saha et al have demonstrated that curcumin in addition to reducing the onset of seizures also reduces oxidative stress and prevents the destruction of brain cells; thereby exerting its neuroprotective effect.
What does this mean?
Curcumin protects the brain from inflammation, toxicity, oxidative damage, drug induced toxicity and also normalizes brain chemicals. This can help in normalizing changes in behaviour, gait and vision that occurs as a result of brain tumor in dogs.
Dosage
Most pet owners and vets state that weight does not play a significantly large role in ascertaining the turmeric dose.
However, it is quite likely that a larger breed would require a larger amount of turmeric to reach the required therapeutic efficacy.
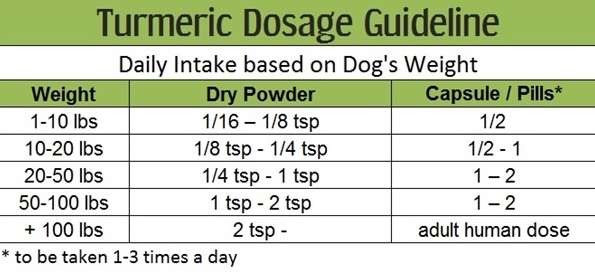
The following table can guide you with the dose of turmeric as per your pet’s weight:
Based on the table you can ascertain the amount of turmeric powder your dog should get as per his weight. Always go for good organic turmeric powder and refrain from giving capsules or pills.
After deciding the amount of turmeric powder and dosage go for the following recipes:
The Golden Paste
This is for ½ cup turmeric powder. Take ½ cup turmeric powder and 1 cup water in a pan and gently stir over a low flame. This can take 7-10 mins. Adjust the water quantity based on the thickness of the paste.
Add 1 ½ teaspoon of freshly ground black pepper and 70 ml coconut or olive oil. Cook till all ingredients are mixed well.
Based on the table above you can start with small doses (1/4 to ½ teaspoon based upon the dog’s weight) and slowly build the dose based on your pet’s tolerance. 1-2 teaspoon twice a day seems good.
There is no such set dosage of turmeric for canine brain tumor but we have covered the details of turmeric dosage for dogs in Turmeric Dosage For Dogs-The Definitive Guide.
Precautions
Always start your pet on small doses and build the dose gradually over weeks. If you observe any side effects discontinue turmeric.
Some say that black pepper can irritate stomach lining of dogs, while some pet owners have not seen any such side effects. So please see if your dog can tolerate turmeric with black pepper or give him turmeric with fat only. That will still make turmeric bioavailable in his body.
Dietary turmeric should not pose any problem buta if you are skeptic please avoid it prior to any surgical procedure that your pet may be scheduled for.
Turmeric is said to work as binding agent so do add lots of water while feeding turmeric to avoid constipation.
If your pet is pregnant, turmeric might act as a mild uterine stimulant so it is advisable to avoid turmeric then. However there is no study which proves this.
Consult a vet before starting your pet on turmeric.
Conclusion
Scientific evidences show that curcumin can exert anti-cancer activity in as many 8 types of brain cancer. It also increases the therapeutic effect of chemotherapeutic drugs and also protects from the side effects.
Occurrence of seizures is a common symptom of brain tumors; curcumin is a natural anticonvulsant agent. Overall turmeric and curcumin protect the brain from damage which warrants the use of turmeric as an adjuvant therapy in brain tumor in dogs.